
Statistics brings fur seal foraging trips into focus
For northern fur seals, a foraging trip in the Bering Sea can span hundreds of miles and last a week or more. This extraordinary journey offers scientists a unique opportunity to track the seals using high-tech devices that measure their location, position, and speed in the water.
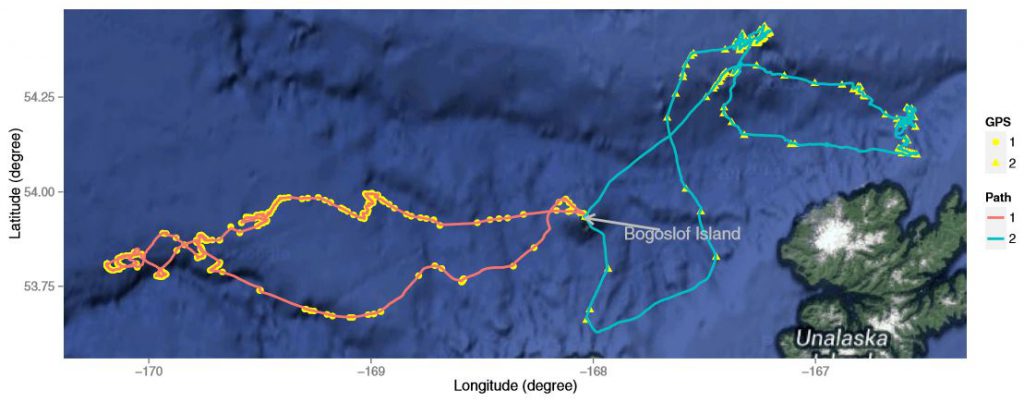
Two feeding trips made in late July by two female northern fur seals tagged on Bogoslof Island. The dots and triangles are GPS observations, and the lines joining them are the reconstructed swimming paths calculated using the Bayesian Melding approach. The trip on the left was 7 days, and the one on the right lasted 7.6 days.
The devices record an enormous amount of data that enables researchers to reconstruct the seals’ routes using a calculation called ‘dead reckoning.’ However, this method does not account for sources of uncertainty in the data, and it can yield inaccurate results.
New Consortium research led by Yang (Seagle) Liu (University of British Columbia) and his supervisor Prof. James V. Zidek has produced a new statistical method that provides a more accurate picture of the actual routes taken. The study was published in the journal Animal Biotelemetry.
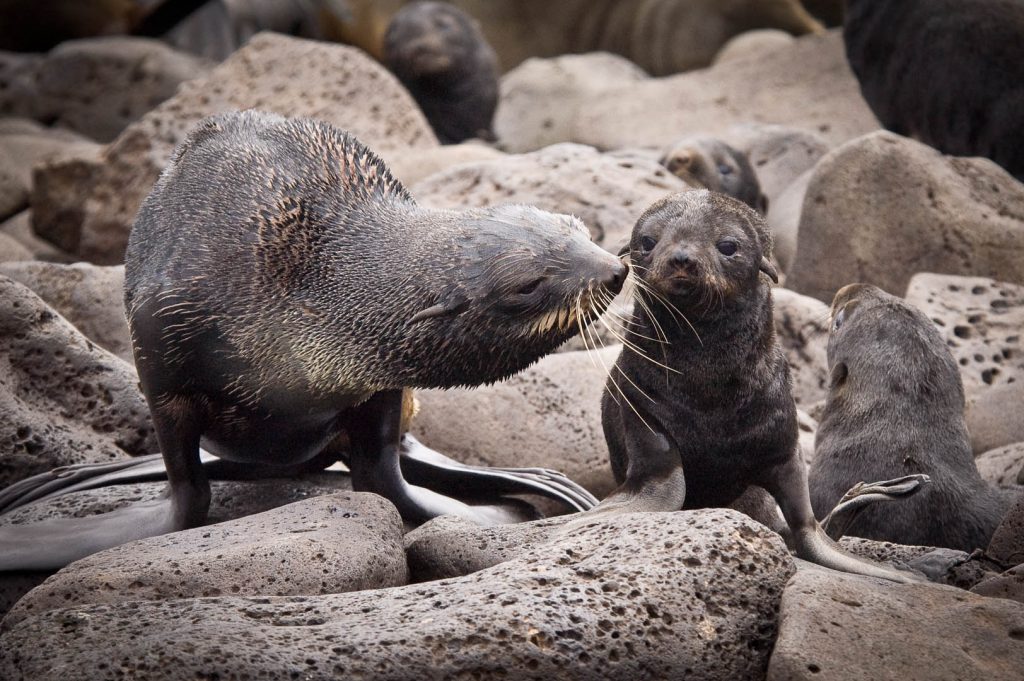

After a week-long feeding trip, a female fur seal that has just returned to the rookery verifies by smell whether the hungry pup that called out to her is hers.
Understanding Uncertainty
“We were presented with a huge data set from two northern fur seals who each undertook a very long foraging trip,” explains Liu. “Generally, statisticians like to work with as much data as possible—but the seals collected more data than what our computers could process all at once.”
“The data was also ‘biased’, or heavily influenced, by environmental variables like ocean currents and gravity, and by the limitations of the devices themselves,” Liu advises. When reconstructing the path, he needed to consider these factors and make the appropriate course corrections.
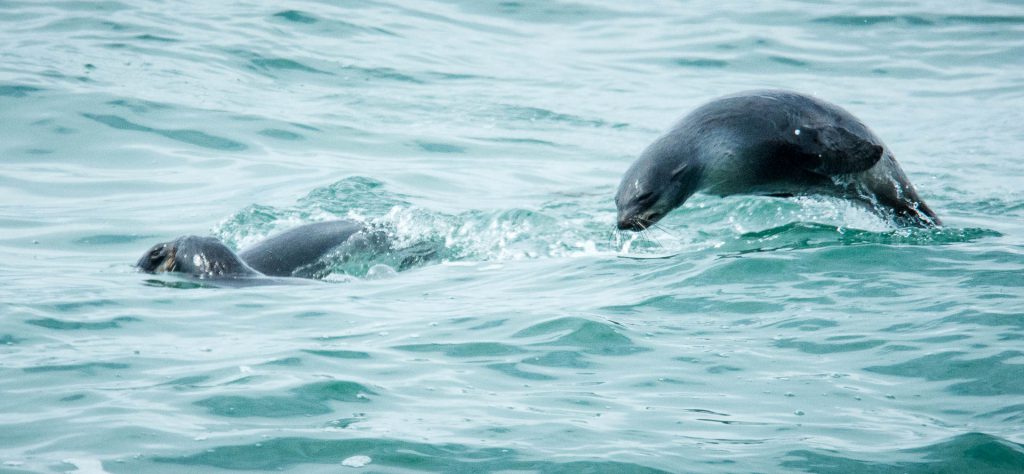

Females often ‘porpoise’ when traveling, and sleep very little during their long foraging trips.
“Fur seals nursing pups always return to the same place they began their foraging trip to reunite with their pups,” says Liu. “From a statistical perspective, this inspired me to use a Brownian Bridge model, in which two ends are fixed and the middle part is random.”
Liu’s statistical method attacked two inherent problems in reconstructing the foraging path: the unknown biases (i.e., from ocean currents, gravity, or equipment) and the accumulation of that bias over time, which produces ever-larger errors in distance.
Correcting Convention
“Our next problem was how to make an inference to predict where the animal would go next,” Liu says. “The huge amount of data required more computing power than most scientists have available, so we found a way to chop the whole trip into small sequences and try to control the chopping points”
When Liu’s results were cross-validated, he discovered his method was able to reconstruct the animals’ movements more accurately than the conventional dead-reckoning calculation, correcting the overall distance traveled by more than 100 kilometers (62 miles).
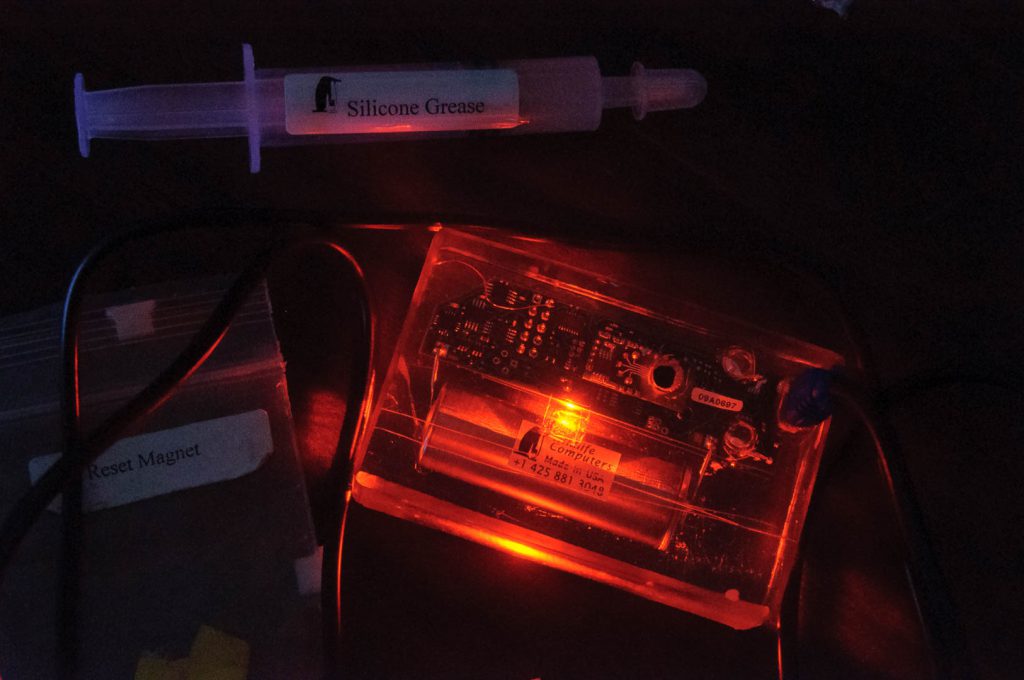

Daily-Diary biologging tag manufactured by Wildlife Computers. The tag recorded depth, light levels, motion (3 dimensional acceleration), attitude (3 dimensional magnetometry), and water temperature. Data downloaded from the tag were used to reconstruct the swimming paths and locations of northern fur seals feeding in the Bering Sea.
“This study presented a unique opportunity to make accurate predictions of an animal’s location based on the combination of large, high-resolution data sets and good statistical methods,” Liu says. “Our model corrected the uncertainty in conventional methods, and demonstrated that the animal’s path is lengthier using conventional analysis than it actually is.”
The new statistical technique developed by Lui and colleagues is a significant advancement in animal tracking. Their method calculates confidence limits for animal tracks, and provides a means to assess the accuracy of satellite-reported locations of animals at sea.
 PUBLICATIONS
PUBLICATIONS
|
|

 |
||||||||||||
|
|

 |
||||||||||||
